Inverse Design of Nonlinear Mechanics of Bio-inspired Materials Through Interface Engineering and Bayesian Optimization
Abstract
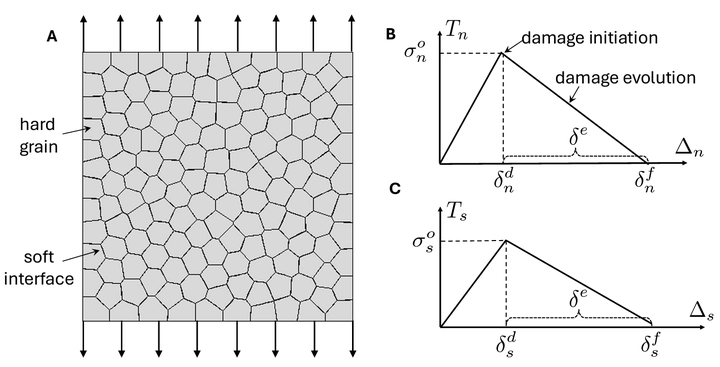
In many biological materials such as nacre and bone, the material structure consists of hard grains and soft interfaces, with the interfaces playing a significant role in the material’s mechanical behavior. This type of structures has been utilized in the design of various bio-inspired composite materials. Such applications often require the materials to exhibit a specified nonlinear stress-strain relationship. A key challenge lies in identifying appropriate interface properties from an infinite search space to achieve a given target stress-strain curve. This study introduces a Bayesian optimization (BO) framework specifically tailored for the inverse design of interfaces in bio-inspired composites. As a notable advantage, this method is capable of expanding the design space, allowing the discovery of optimal solutions even when the target curve deviates significantly from the initial dataset. Furthermore, our results show that BO can identify distinct interface designs that produce similar target stress-strain responses, yet differ in their deformation and failure mechanisms. These findings highlight the potential of the proposed BO framework to address a wide range of inverse design challenges in nonlinear mechanics problems.